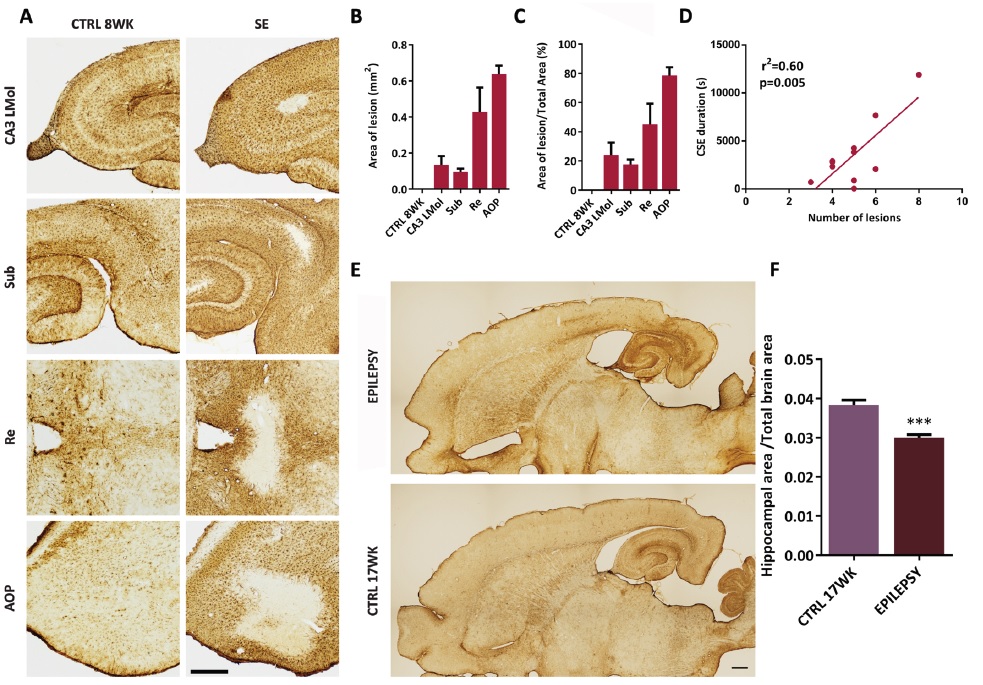
Fig. 4. Lesioned areas and hippocampal atrophy in kainic acid (KA) model. Brain sections were stained against mouse anti-glial fibrillary acidic protein (GFAP), a marker of astrocytes, which are absent in lesioned areas (A). Comparing to control group (CTRL) of 8 weeks (WK), the KA treatment induced GFAP-immunonegative areas in CA3 stratum lacunosum-molecolare (CA3 LMol), subiculum (Sub), nucleus reuniens (Re) and anterior olfactory nucleus (AOP) (B). In C, the percentage of lesion area of the total area was also determined in CA3 LMol, Sub, Re and AOP. In D, the linear regression (r▓) between the number of damaged brain areas and mean duration of convulsive seizures during status epilepticus (SE) was also determined. The hippocampal atrophy of 64-week-old rats (E) was measured in F. Quantification of the area was performed using the image analysis software NIS-Elements. Statistical analysis was performed using a linear regression analysis and a Student's t-test. Data are shown as mean ▒ SEM. ***p<0.001; Scale bars: 500 μm and 1 mm. CSE, convulsive status epilepticus.